Threat modeling is a process used to identify and prioritize potential threats to a system or organization. By understanding the potential risks and vulnerabilities, organizations can take steps to mitigate or prevent them.
One popular method for threat modeling is the STRIDE approach, which stands for Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information disclosure, Denial of service, and Elevation of privilege. This method helps organizations identify potential threats and understand the impact they could have on the system or organization.
Another popular method is the PASTA approach, which stands for Process for Attack Simulation and Threat Analysis, it is a structured approach to identify, quantify, and prioritize threats. It begins with understanding the architecture of the system and identifying the assets that need to be protected. The next step is to identify the potential attackers and their motivations. Finally, the organization simulates attacks and evaluates the impact they could have on the system.
Threat Modeling Process
- Identify the valuable assets that the system must protect
- Use tables and the Microsoft threat modeling tool to document the architecture of the application, including subsystems, trust boundaries, and data flow
- Decompose the architecture of the application, including the underlying network and host infrastructure design, to create a security profile for the application; the aim of the security profile is to uncover vulnerabilities in the design, implementation, or deployment configuration of the application
- Keeping the goals of an attacker in mind, and with knowledge of the architecture and potential vulnerabilities of the application, identify the threats that could affect the application
- Document each threat using a common threat template that defines a core set of attributes to capture for each threat
- Rate the threats to prioritize and address the most significant threats first; the rating process weighs the probability of the threat against damage that could result should an attack occur; it might turn out that certain threats do not warrant any action when you compare the risk posed by the threat with the resulting mitigation costs
Defect Dojo – Threat Modeling Example
Defect Dojo is an open-source vulnerability management tool that helps organizations track and manage security vulnerabilities. It provides a centralized platform for managing and reporting on vulnerabilities, tracking remediation efforts, and managing penetration testing engagements. Defect Dojo allows organizations to import vulnerabilities from a variety of sources, including scanners and manual findings, and provides a number of features for prioritizing and managing vulnerabilities, including risk scoring and reporting. Additionally, it offers integration with other tools such as Jira, Slack, and GitLab. Defect Dojo is designed to be easy to use and customizable, making it a popular choice for organizations of all sizes.
Step 1 – Identify Assets
- Products Information – Stores information related to different products that would undergo security testing. This includes information of the product and its features.
- Vulnerability Findings – Stores information about the vulnerabilities found in products during security testing.
- User Credentials – Stores information of user authentication credentials and includes usernames and passwords.
- Test Results – Stores success and failure scenarios of security tests performed on a product. It also includes information about false positives.
- Vulnerability Reports – All true positive findings of a security testing on a product exported as a report and stored as a pdf / word / excel on the server.
- Database Credentials – The web application, to access database stores credentials
- Web Server – The host and the application server that runs the web application
- Application Notification Configurations – Application sends notifications to users through Email, Slack, MS Teams and other channels for which it stores the API keys for each of the integrations.
- API Endpoints – API Endpoints to serve data to requests from the web UI or the browser.
- Web UI – An interface for users to interact with the application.
Step 2 – Create an architecture diagram
Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool is a tool that helps organizations identify and mitigate potential security threats by creating detailed architecture diagrams of their systems. It provides several templates for different systems and allows for customization, it also allows for automated threat analysis and prioritization of identified vulnerabilities. It also generates a report that can be used to communicate the security posture of the system to stakeholders and management. The tool helps organizations design and plan secure systems.
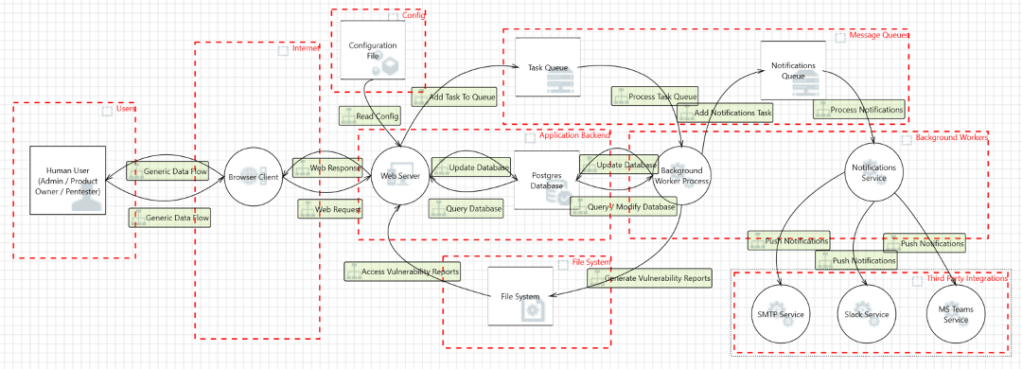
Step 3 – Document the security profile
A security profile is a set of security measures and controls that an organization puts in place to protect its assets and data. These measures may include things like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and access controls. A security profile can also include policies and procedures for incident response, disaster recovery, and employee training. The goal of a security profile is to provide a comprehensive approach to security that covers all the critical areas of an organization’s operations. It is important for organizations to regularly review and update their security profiles to ensure that they are aligned with the latest security best practices and threats.
Few examples are as shown below –
| Categories | Threat Considerations |
| Input validation | Is all input data validated? Could an attacker inject commands or malicious data into the application? Is data validated as it is passed between separate trust boundaries (by the recipient entry point)? Can data in the database be trusted? |
| Authentication | Are credentials secured if they are passed over the network? Are strong account policies used? Are strong passwords enforced? Are certificates being used? Are password verifiers (using one-way hashes) used for user passwords? |
| Authorization | What gatekeepers are used at the entry points of the application? How is authorization enforced at the database? Is a defense in depth strategy used? Do you fail securely and only allow access upon successful confirmation of credentials? |
| Configuration management | What administration interfaces does the application support? How are they secured? How is remote administration secured? What configuration stores are used and how are they secured? |
| Sensitive data | What sensitive data is handled by the application? How is it secured over the network and in persistent stores? What type of encryption is used and how are encryption keys secured? |
step 4 – identify threats
Threat identification can take any of the below mentioned forms –
Stride Approach
The STRIDE approach is a method used in threat modeling to identify and prioritize potential security threats. It stands for Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information disclosure, Denial of service, and Elevation of privilege. This method helps organizations identify potential threats and understand the impact they could have on the system or organization. Each category of the acronym represents a different type of threat, such as Spoofing for impersonation, Tampering for unauthorized modification, Repudiation for denying actions, Information disclosure for unauthorized access, Denial of service for disrupting availability and Elevation of privilege for unauthorized actions. By identifying potential threats in each category, organizations can take steps to mitigate or prevent them, helping to protect their assets and maintain the trust of their customers.
| Property | Threat Definition | Examples | Mitigations |
| Tampering | Potential Persistent Cross-Site Scripting | An adversary can store malicious javascript code into the database and can obtain the cookie values of logged in users who visit the affected pageAn adversary can deface the application making it look like a login page thereby obtaining user credentials | Perform input validationContext based output encoding (HTML, JavaScript, CSS and others)HTML sanitizationSet cookie attributes like secure and HttpOnly |
categorized threat lists Approach
Categorized Threat Lists (CTL) is a method of organizing and prioritizing potential security threats based on their likelihood and impact. This method creates a list of threats that are grouped into different categories, such as high, medium, or low risk. This allows organizations to prioritize their efforts and focus on the most critical threats first. Categorized Threat Lists are often used in conjunction with other threat modeling methods, such as STRIDE or PASTA, to provide a more comprehensive approach to identifying and mitigating security risks. These lists can also be used to track the progress of remediation efforts and report on the current state of an organization’s security posture. CTLs are also useful for communication and education of the threat landscape for stakeholders, allowing them to understand risks and take appropriate action.
| Name | Description | Countermeasures |
| Authentication | Attacks on authentication is usually known as Spoofing – an attacker tries to impersonate another user thereby leading to unauthorized disclosure of information. Brute force method to break authentication is one of the most common methods to login as another user. In addition, stolen credentials, broken authentication and default credentials allows attackers to not only gain access to other users, but also to administrative interfaces | Implement strong authentication mechanisms and ensure strong password policyImplement strong password hashing to avoid password leakageEnforce rate limiting, Captcha and Multi Factor authentication to prevent brute force attacksEnsure to use certificates to prove the authenticity of sender and receiver |
Relevant attack patterns approach
Relevant attack patterns are specific tactics, techniques and procedures used by attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in a system or organization. They are identified through threat modeling or threat intelligence and are specific to the environment of the organization. By identifying these attack patterns, security teams can focus their efforts on the most at-risk areas and develop effective countermeasures. They also can be used to train employees and test incident response plans.
| Goal: Exploit the potential SQL injection vulnerability to compromise the confidentiality and integrity of data in the database Precondition: Attacker provides inputs which are used to build an SQL query without validation Attack: 1. Identify user input parameters on the target system susceptible to SQL injection 2. Construct an input value that has some malicious SQL queries 3. Send a request with the malicious input to the application leading to execution of malicious queries on the database Postcondition: Target system executes the malicious SQL queries on the database |
| Goal: 1. Potential Elevation of Privilege Using Remote Code Execution Precondition: Web server processes malicious files from the file system without validation Attack: 1. Identify the file processing feature of the application 2. Construct a malicious file that executes when processed by the web server 3. Upload the malicious file to the file system 4. Trigger the file processing feature to read the malicious file thereby executing commands remotely Postcondition: Target system executes the commands leading to Remote Code Execution |
Attack Trees Approach
Attack trees are a method of visualizing and analyzing potential attack paths against a system or organization. They are a type of decision tree that starts with a high-level attack goal and branches out into specific tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) used to achieve that goal. They are useful for identifying potential vulnerabilities and understanding the potential impact of different types of attacks, and also for evaluating the effectiveness of different security controls and countermeasures.
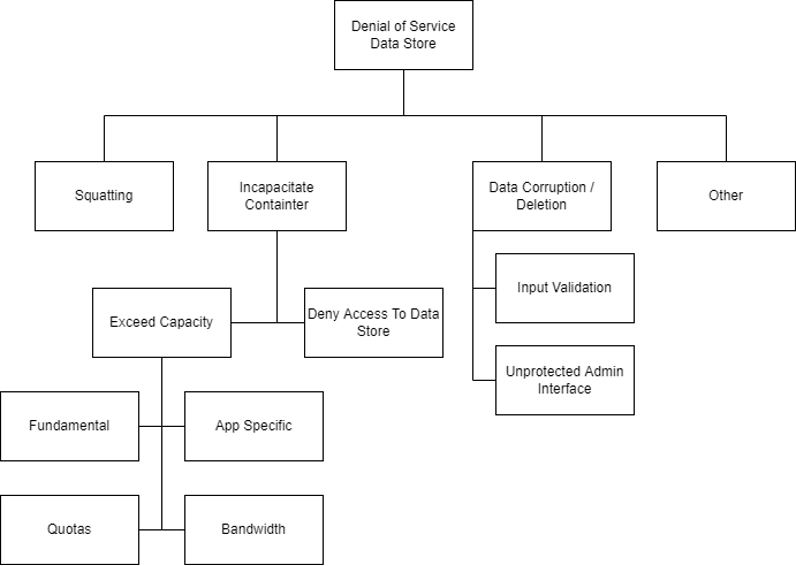
Example of Denial of Service to Data Store using Attack Trees Approach
Step 5 – document and rate threats
| Threat Description | Information Disclosure Data Store |
| Threat target | Web application Database |
| Risk | High |
| Attack techniques | Remote Attack |
| Countermeasures | Enable Authentication, Firewall Rules, Private Networks |
| Threat Description | Cross Site Scripting |
| Threat target | Web Application Front End |
| Risk | Medium |
| Attack techniques | Input parameter tampered with malicious JavaScript |
| Countermeasures | Output Encoding, HTML Sanitization, Input validation |
| Threat Description | Authentication Attacks |
| Threat target | Application Authentication Mechanism |
| Risk | Medium |
| Attack techniques | Brute Force Attacks, Stolen Credentials |
| Countermeasures | Protection against brute force attacks |
Conclusion
Threat modeling can be an ongoing process, with organizations regularly reviewing and updating their models as new threats emerge. One of the main benefits of threat modeling is that it helps organizations focus their security efforts on the areas that are most at risk. By identifying potential threats early on, organizations can take steps to prevent them from happening.
In addition to identifying and preventing threats, threat modeling can also help organizations understand the trade-offs they may need to make between security and functionality. It can also help organizations identify areas where they may need to invest in new technologies or processes to better protect their systems.
In summary, threat modeling is an important step in ensuring the security of a system or organization. By identifying and prioritizing potential threats, organizations can take steps to mitigate or prevent them, helping to protect their assets and maintain the trust of their customers.
